Petrous Apex Disease
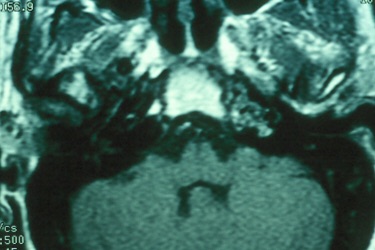
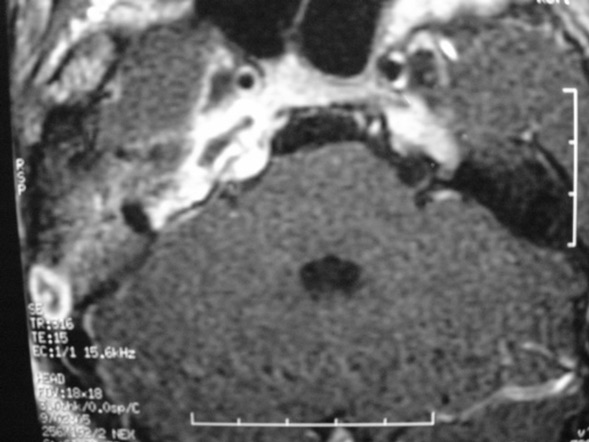
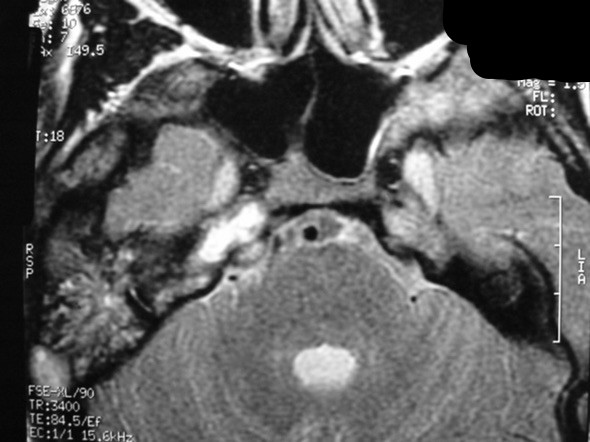
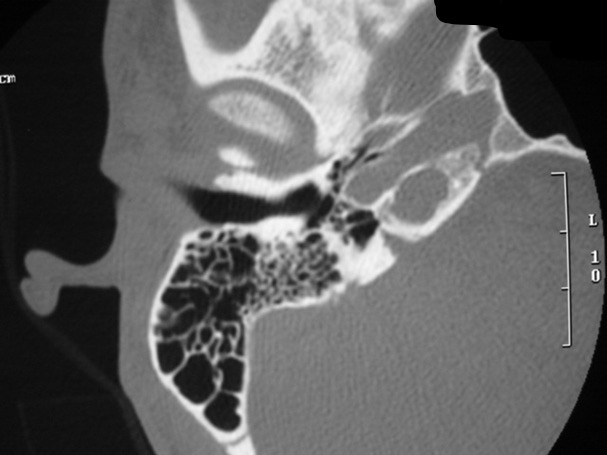
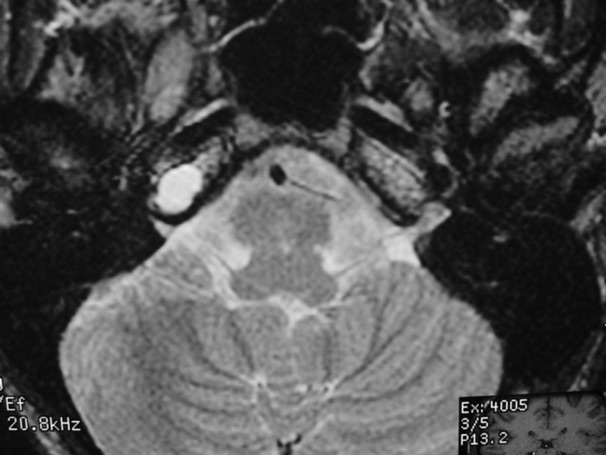
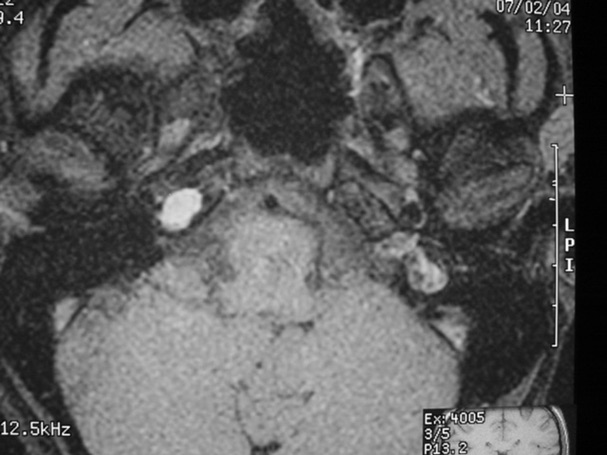
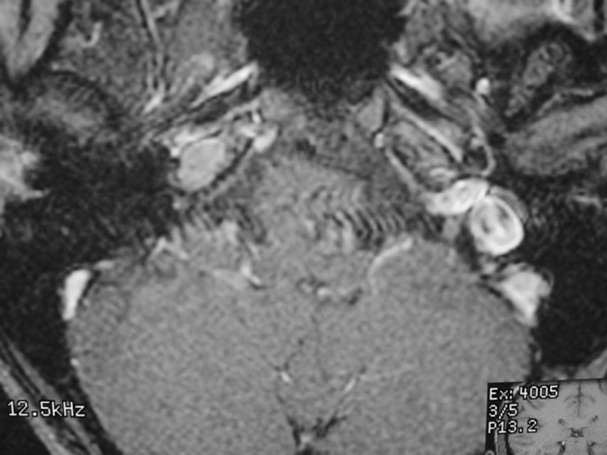
The petrous apex is a relatively inaccessible area that can occasionally harbor serious disease. Disease processes that usually cause symptoms are typically inflammatory or neoplastic in nature. Petrous apex lesions typically cause nonspecific symptoms such as headache, but as the lesion becomes more extensive, adjacent structures such as cranial nerves can become involved. A common early and specific sign of a petrous apex process is abducens palsy. Current imaging techniques can usually provide enough supplemental information to allow a focused plan of treatment. It is important to determine whether a petrous apex lesion can be observed or, if surgical treatment is required, whether a drainage or excision is required. There are various available surgical approaches to the petrous apex. The choice depends on the status of hearing function as well as the suspected pathology, which will dictate whether a drainage or excisional procedure is required.
- Review the anatomy of the petrous apex.
- Recognize the signs and symptoms that suggest the presence of petrous apex disease.
- Describe the normal anatomical variants of this area.
- Summarize the types of pathology that can occur in the petrous apex, the imaging required, and proper interpretation of information so that a proper differential diagnosis can be formulated.
- Formulate a plan of treatment based on clinical findings.
- Explain the various surgical approaches to the petrous apex.
Learner must Sign In to access AAO-HNSF education activities.